-
Posted on
How to publish your Godot game on Mac
Since 2019, Apple has required all MacOS software to be signed and notarized. This is meant to prevent naive users from installing malware while running software from unknown sources. Since this process is convoluted, it stops many indie game developers from releasing their Godot games on Mac. To solve this, this article will attempt to document each and every step of the signing and notarization process.

Photo by Natasya Chen Step 0: Get a Mac
While there tools exists to codesign/notarize Mac executables from other platforms, I think having access to a MacOS machine will remove quite a few headaches.
A Mac VM, or even a cloud machine, might do the job. I have not personally tested those alternatives, so if you do, please tell me if it works well.
Step 1: Get an Apple ID and the Developer App
You can create an Apple ID through Apple’s website. While the process should be straightforward, it seems like Apple has trust issues when it comes to email from protonmail.com or custom domains. Do not hesitate to contact support in case you encounter issues creating or logging into your Apple ID. They are quite responsive.
Once you have a working Apple ID, use it to log into the App Store on your Mac and install the Apple Developer application.
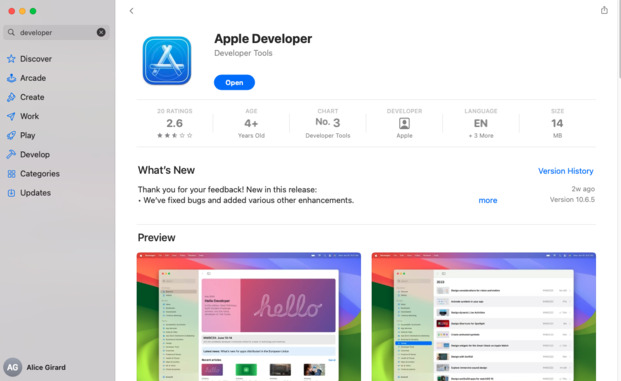
Step 2: Enroll in the Apple Developer Program
Next, open the Apple Developer app, log in, and ask to “Enroll” in the developer program.
This will require you to scan your ID, fill in data about you and your company, and most likely confirm those data with a support agent by phone. The process costs ~99$ and should take between 24 and 48 hours.
Step 3: Setup Xcode
Xcode will be used to codesign and notarize your app through Godot. You should install the app through the App Store like you did for the Apple Developer application.
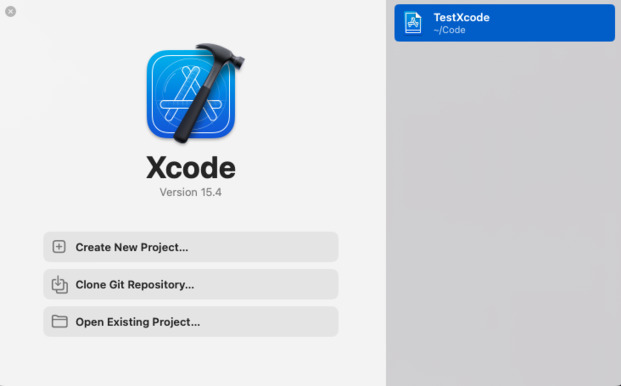
Once the app is installed, we need to accept the license.
First, launch Xcode and close it. Then open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo xcode-select -s /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer sudo xcodebuild -license acceptStep 4: Generate a certificate signing request
To obtain a code signing certificate, we need to generate a certificate request.
To do this, open Keychain, and from the top menu, select Keychain Access > Certificate Assistant > Request a Certificate From a Certificate Authority. Fill in your email address and choose Request is: Saved to disk. Click on Continue and save the .certSigningRequest file somewhere.
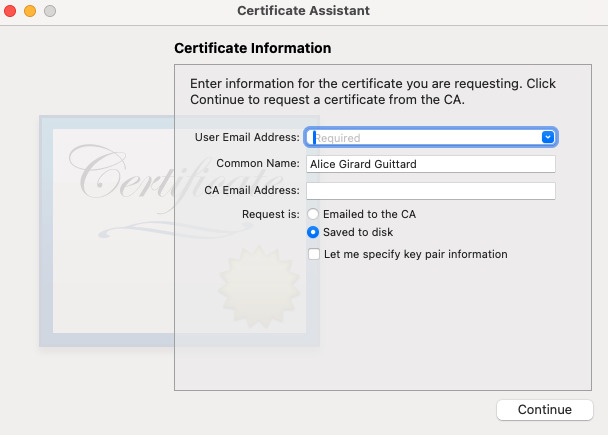
Step 5: Obtain a code signing certificate
Now, head to the Apple Developer website. Log in and go to the certificate list. Click on the + button to create a new certificate. Check Developer ID Application when asked for the type of certificate and click on continue.
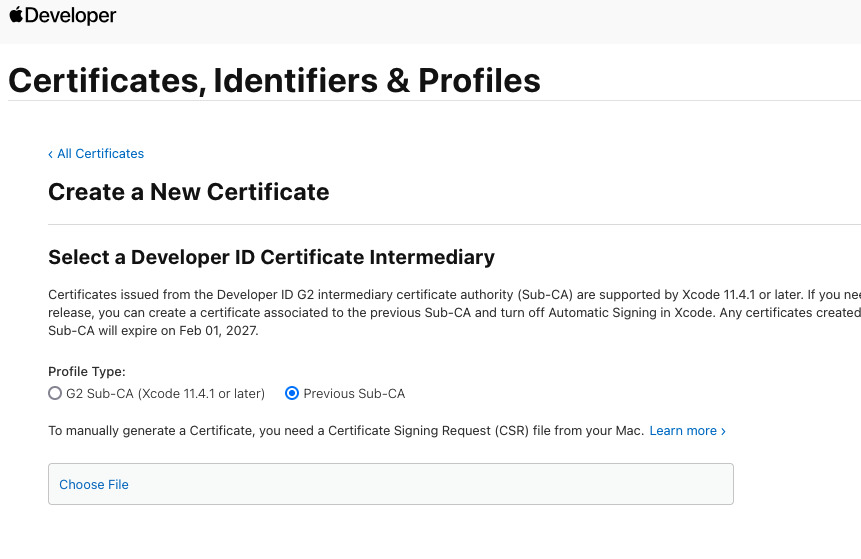
On the next screen, upload the certificate signing request we generated in step 4.
You’ll be prompted to download your certificate. Do it and add it to Keychain by double-clicking on the file.
You can check that your certificate was properly added by running the following command:
security find-identity -v -p codesigningIt should return (at least) one identity.
Step 6: Get an App Store Connect API Key
Back to the Apple Developer website, go to Users and Access, and open the Integrations tab. From this page, you should request access to the App Store Connect API. This access should normally be granted immediately.
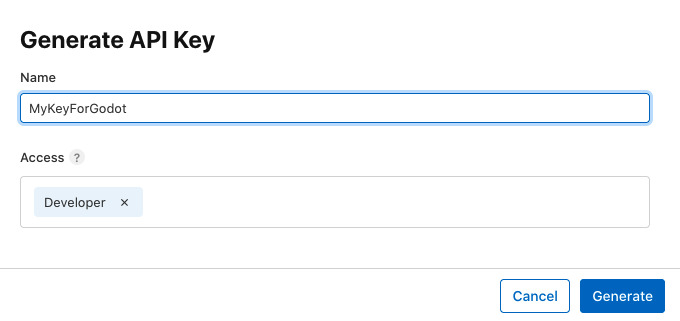
From this page, create a new key by clicking on the + icon. Give your key a name you will remember and give it the Developer access. Click on Generate and the key will be created.
You will then be prompted to download your key. Do it and store the file safely, as you will only be able to download it once.
Step 7: Configure Godot
Open your Godot project and head to the project settings using the top menu (Project > Project Settings). From there search for VRAM Compression and check Import ETC2 ASTC.
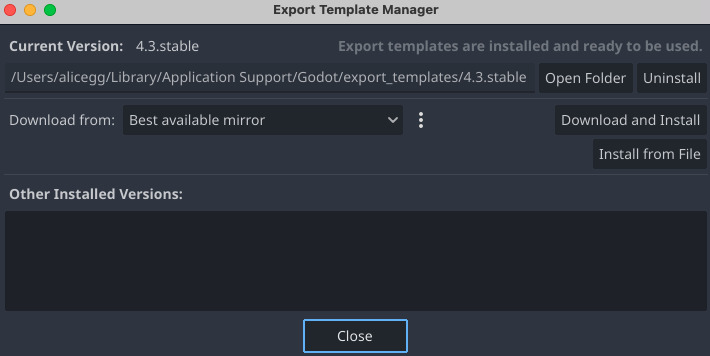
Then make sure you have installed up-to-date export templates by going through the Editor > Manage Export Templates menu and clicking on Download and Install.
To export your project, head to the Project > Export. Click on Add and select macOS to create new presets. In the presets form on the left, you’ll have to fill in a unique Bundle Identifier in the Application section, this can be
com.yourcompany.yourgame.In the Codesign section, select Xcode codesign and fill in your Apple Team ID and Identity. Those can be found using the
security find-identity -v -p codesigningcommand: the first (~40 characters) part of the output is your identity, and the last (~10 characters, between parentheses) is your Team ID.In the Notarization section, select Xcode notarytool and fill in your API UUID (found on the appstoreconnect page), API Key (the file you saved in Step 6), and API Key ID (also found on the appstoreconnect page).
Click on Export Project… to start the export.
Step 8: Checking the notarization status
Godot will automatically send your exported file for notarization.
You can check the notarization progress by running:
xcrun notarytool history --key YOUR_AUTH_KEY_FILE.p8 --key-id YOUR_KEY_ID --issuer YOUR_ISSUER_IDAccording to Apple, the process should rarely take more than 15 minutes. Empirically, this is sometimes very false and the process can give you enough time to grab a coffee, bake a cake, and water your plants.
Once the notarization appears completed (with the status Valid or Invalid), you can run this command to check the result (using the job ID found in the previous command output):
xcrun notarytool log --key YOUR_AUTH_KEY_FILE.p8 --key-id YOUR_KEY_ID --issuer YOUR_ISSUER_ID YOUR_JOB_IDStep 9: Stapling your executable
To make sure that your executable can work offline, you are supposed to ‘staple’ the notarization to it. This is done by running the following command:
xcrun stapler staple MY_SOFTWARE.dmgExtra: Exporting the game as .app
Godot can export your game as .dmg, .zip, or .app. For most users, it is more convenient to receive the game as .app, as those can be directly executed. However, the notarization process doesn’t support uploading .app files to Apple’s server.
I think the proper way to obtain a notarized .app file is to:
- Export the project .dmg from Godot with code signing and notarization
- Mount the .dmg and extract the .app located inside of it
- Staple the .app bundle
Extra: Code signing GodotSteam
GodotSteam is a Godot add-on that wraps the Steam API inside GDscript. If you use it, you might encounter issues during notarization, because it adds a bunch of .dylib and .framework files.
What I did to work around that was to codesign the framework folders:
codesign --deep --force --verify --verbose --sign "Developer ID Application: My Company" libgodotsteam.macos.template_release.framework codesign --deep --force --verify --verbose --sign "Developer ID Application: My Company" libgodotsteam.macos.template_debug.frameworkI also checked the options Allow DyId environment variable and Disable Library Validation in the export settings (section Codesign > Entitlements).
FAQ: Is this really necessary if I’m just going to publish my game on Steam?
Actually, I’m not 100% sure, but I think it is only “recommended” and Steam can bypass the notarization. Steamworks does contain a checkbox asking if App Bundles Are Notarized, so I assume it might do something.
-
Posted on
Create a presskit in 10 minutes with Milou
Talking to the press is an inevitable part of marketing a game or software. To make the journalist’s job easier, it’s a good idea to put together a press kit. The press kit should contain all the information someone could want to write an article about your product, as well as downloadable, high-resolution assets.
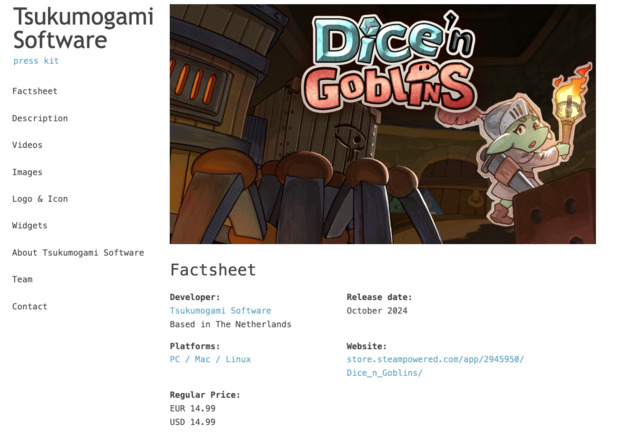
The press kit for our upcoming game Dice'n Goblins Introducing Milou
Milou is a NodeJS software that generates press kits in the form of static websites. It aims at creating beautiful, fast, and responsive press kits, using only YAML configuration files.
I built it on top of presskit.html, which solved the same problem but isn’t actively maintained at the moment. Milou improves on its foundation by using a more modern CSS, YAML instead of XML, and up-to-date Javascript code.
Installation
First, you will need to have NodeJS installed:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.7/install.sh | bash nvm install 22Once Node is ready, you can use NPM to install Milou:
npm install -g milouRunning
milou -Vshould display its version (currently 1.1.1).Let’s build a press kit
Let’s create a new project:
mkdir mypresskit cd mypresskit milou newThe root directory of your project will be used for your company. In this directory, the file
data.ymlshould contain data about your company, such as your company name, location, website, etc… You can find an example of a fully completed companydata.ymlfile on GitHub. To validate that your file is a valid YAML file, you can use an online validator.Your company directory should contain a sub-folder called
images, you should put illustrations you want to appear in your press kit inside it. Any file namedheader.***will be used as the page header,favicon.icowill be used as the page favicon, and files prefixed by the wordlogowill appear in a dedicated logo section of the page (eg.logo01.pngorlogo.jpg). Other images you put in this folder will be included in your page, in the Images section.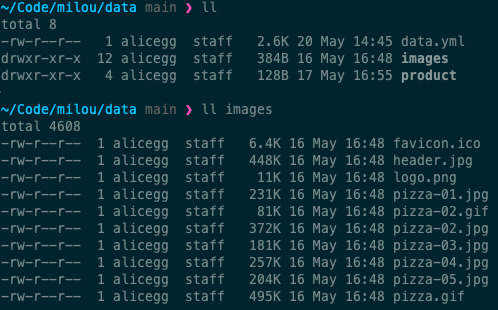
The directory structure After completing your company page, we can create a product page. This will be done in a subfolder:
mkdir myproduct cd myproduct milou new -t productJust like for a company, you should fill in the
data.ymlfile with info about your product, like its title, features, and prices. You can find an example of a product file on GitHub. The product folder should also contain animagessubfolder. It works the same way as for the company.
The example press kit When your product is ready, go back to the company folder and build the press kit:
cd ../ milou build .This will generate the HTML and CSS files for your online presskit in the directory
build. You can then use any web server to access them. For example, this will make them accessible fromhttp://localhost:3000/cd build npx serveTo put your press kit online, you can upload this folder to any static site host, like CloudFlare Pages, Netlify, or your own server running Nginx.
Conclusion
Milou is still quite new, and if you encounter issues while using it, don’t hesitate to open an issue. And if it works perfectly for you, leave a star on GitHub.
-
Posted on
How to solve it (with raycasting)
In 1945, mathematician George Pólya released the book “How to solve it”. It aims at helping math teachers guide their students into solving abstract problems by asking the right questions. It has since had a large influence on math education and computer science, to the point of being mentioned by Marvin Minksy as a book that everyone should know.
In this post, I will try to see how we can use Pólya’s methodology to solve a concrete software engineering problem: rendering 3D objects (using Golang).
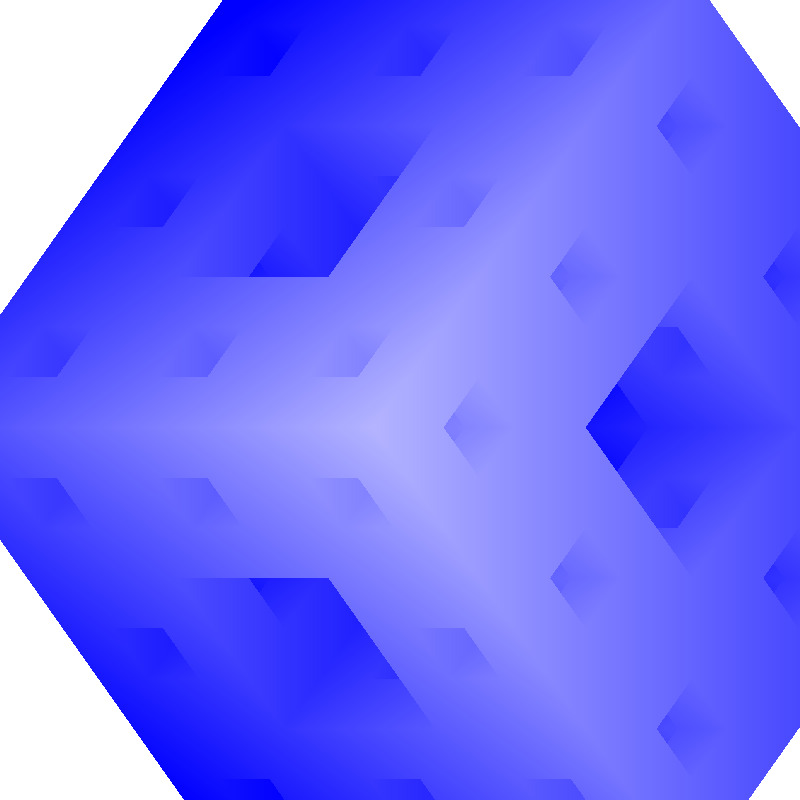
Understanding the problem
Before starting to solve the problem, we must make sure that we completely understand the problem. The first question to ask ourselves is What is the data?
The data is a 3D object. The object is made out of triangles. Each triangle is made out of 3 vertices (and a normal vector). Those objects are stored in .STL files. I will parse them with the hschendel/stl lib.
The second question, which is probably the most important is What is the unknown?. Or in programming terms, What should the program output?
Our program should output an image. An image is a 2D matrix of pixels, each pixel representing a color. The most common way of representing color is the RGBA model, which stands for Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha. In Golang, images can be represented using the
image.Imagedata structure from the standard library.The third question is What is the condition (linking the data to the output)?
The data gives us information about the space occupied by our 3D object. If the 3D object is in front of our pixel, this pixel should be in a different color. We will use the method known as “raycasting” which consists of sending a ray from each pixel, and checking what the ray hits.
Devise a plan
Now that we have understood our problem a little bit better, we should try to plan what our solution will look like. The most helpful question to come up with a solution is Do you know a related problem?
Raycasting constists of sending a “ray” for each pixel of our image. If this ray intersects with our 3D object, the pixel needs to be updated to a different color. Since our 3D object is made entirely out of triangle, a related problem would be Does a vector intersect with a triangle?
To solve this we can implement the Möller–Trumbore intersection algorithm. This algorithm transforms the above problem into two new questions Does the ray intersect with the triangle’s plane? and if yes, Does the ray-plane intersection lie outside the triangle?
This first question is simple to solve, the only way a vector doesn’t intersect with a plane is if the vector and plane are parallel. In that case, the dot product of the ray and the triangle’s normal vector would be zero, since the dot product of two perpendicular vectors is 0 and the normal vector is itself perpendicular to the triangle’s plane.
If the ray intersects with our triangle’s plane, then we can check if the intersection is inside the plane by switching to barycentric coordinates. Barycentric coordinates are a way to represent a point in a plane in relation to the vertices of the triangle. Each corner of the triangle will get the coordinates (0,0,1), (0,1,0) and (1,0,0). Any point outside of the triangle will get coordinates outside of the range [0,1].
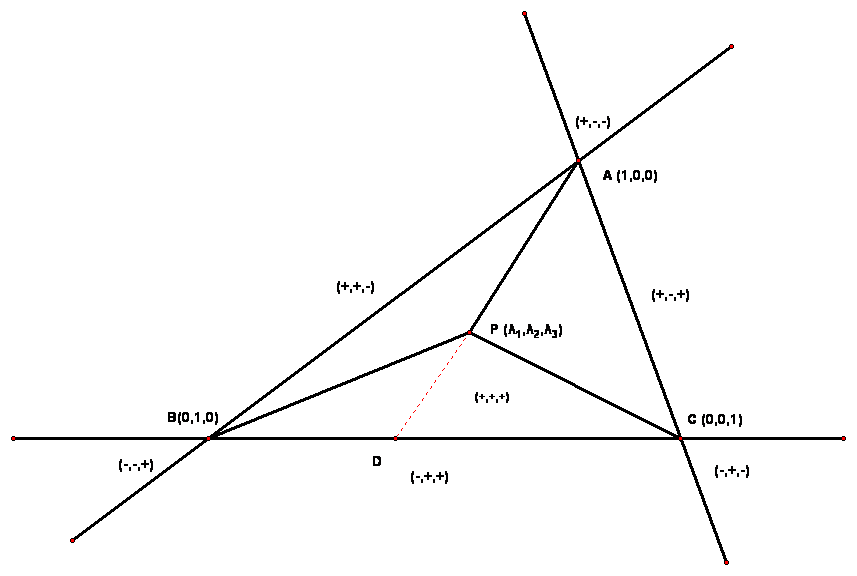
Visualizing barycentric coordinates Now that we know an algorithm that can solve our main issue, we can come up with the outline of our program:
func MTintersect(ray, triangle) bool { if isParallel(ray, triangle) { return false } u , v := projectBaryocentric(vec3, triangle) return u > 0 && u < 1 && v > 0 && u + v < 1 } func main () { solid := readSTL() image := newImage(width, height) for i := range width { for j := range height { image.Set(i, j, white) ray := castRay(i, j) for triangle := range solid.Triangles { ok := MTintersect(ray, triangle) if ok { image.set(i, j, blue) } } } } writePNG(image) }Carrying out the plan
This is the easy part. We just write the code.
The main suggestion that Pólya makes, is to check that every step of the solution is correct. While programming, this can be achieved by writing unit tests to ensure the correctness of our code.
Looking back
Once we have something that seems to work it is tempting to just
git pushand call it a day. But there are a few more questions we should ask ourselves.First Can we check the result?
A good way to answer that is to test our program ourselves, either by manually going through a checklist or by writing an integration test that covers our problem.
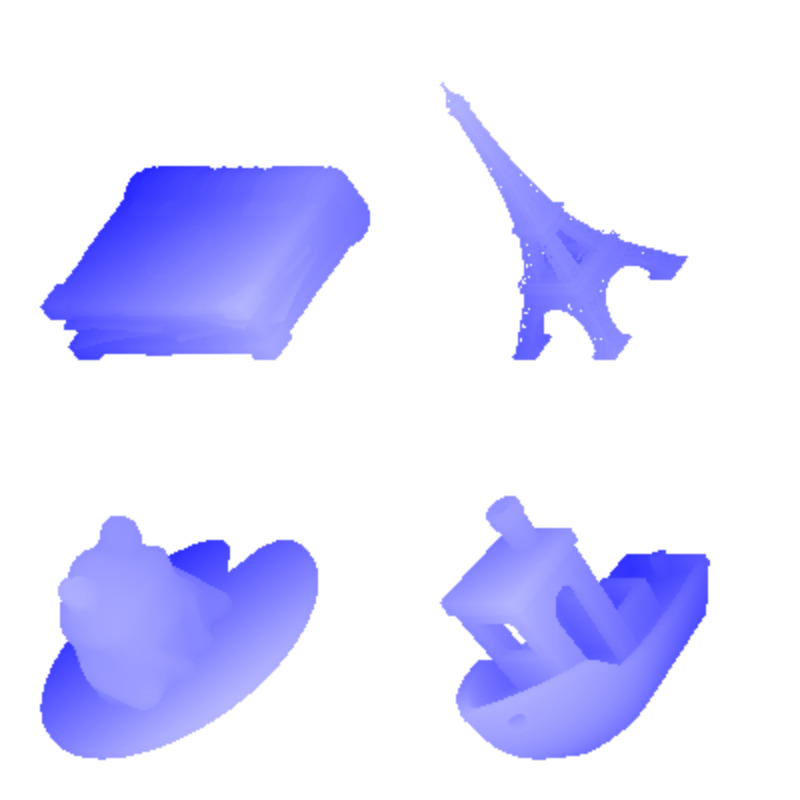
Results of rendering a few .stl files Then we should ask ourselves Can we derive the result differently?
This question is not only a good way to learn about other ways to solve our problem (like Scanline rendering in our case) but also a good opportunity to check if maybe the code we wrote was not the most intuitive solution and could be refactored.
The last question is Can you use the result for another problem?
We can answer this question by checking if our code is written in a way that is reusable enough if we ever want to. For example, the raycaster above could be used as the first step into the implementation of a more sophisticated ray tracing algorithm, if we wanted to handle reflections and lightning.
Conclusion
If you want to check the source code for the raycaster I made before writing this article, it is on my GitHub.
You can find How to solve it by Pólya in any good library.
To learn more about computer graphics check out Ray Tracing in a weekend. And for the details of the Möller-Trumbore algorithm, this video is the one that made the most sense to me.
-
Posted on
A love letter to Apache Echarts
In the world of software development, I believe the 7th circle of hell is called “NPM”. It’s a place where you can find Javascript libraries that make great promises only to disappoint you once you actually import them. I know this because I even wrote one.
When you find a gem hidden in this pile of garbage, it is important to tell the world about it. So, I am here to tell you how much I love Apache Echarts.
A flow visualization from the Echarts examples What is this Echarts thing about?
Apache Echarts is a data visualization library made by researchers from Zhejiang University and Baidu. It provides developers with a declarative language that helps you render charts to canvas or SVG elements.
What makes it stand out from other charting libraries is that it manages to cover a very wide range of use cases while remaining simple to use. On top of that, the documentation never failed to point me in the right direction. And most importantly, the results look good and are interactive.
A few examples
Bar chart
To get started, let’s do a simple bar chart of the stars in my GitHub repositories in 20 lines of code.
Source code
const bar = echarts.init(document.getElementById('bar')); bar.setOption({ legend: {}, tooltip: {}, dataset: { // dataset.source contains your data in table form source: [ ['repo', 'stars'], ['Mikochi', 129], ['crud_benchmark', 40], ['sql-repository', 7], ], }, xAxis: { // category will use the first column for the x axis type: 'category', }, yAxis: {}, series: [ // this creates a bar chart { type: 'bar' }, ], });
Financial chart
If like me, you enjoy playing with financial data, you might be used to more complex charts. Echarts lets you easily combine multiple visualizations in the same canvas. The following chart uses candlesticks to visualize price fluctuations, a line for the averages, and bars for the volume.
Source code
const candles = echarts.init(document.getElementById('candles')); candles.setOption({ title: { text: 'Apple Inc. Week 6 2024' }, tooltip: {}, dataset: { source: [ ['date', 'close', 'open', 'lowest', 'highest', 'volume', 'sma50'], ['2024-02-09', 188.85, 188.65, 188.00, 189.99, 45155216.0, 190.48], ['2024-02-08', 188.32, 189.38, 187.35, 189.54, 40962047.0, 190.51], ['2024-02-07', 189.41, 190.64, 188.61, 191.05, 53438961.0, 190.54], ['2024-02-06', 189.30, 186.86, 186.77, 189.31, 43490762.0, 190.55], ['2024-02-05', 187.68, 188.15, 185.84, 189.25, 69668812.0, 190.59], ], }, xAxis: { type: 'time', // automatically parses the dates }, yAxis: [ // scaled axis for the price { name: 'Price', scale: true }, // hidden axis for the volume { max: 150000000, scale: true, axisLabel: { show: false }, axisLine: { show: false }, splitLine: { show: false }, }, ], series: [ // this creates a candlestick chart using cols [0-5] { type: 'candlestick', yAxisIndex: 0, tooltip: { formatter: (param) => ` Date: ${param.value[0]}<br /> Open: ${param.value[2]}<br /> High: ${param.value[4]}<br /> Low: ${param.value[3]}<br /> Close: ${param.value[1]}<br /> `, }, }, // the volume gets mapped to a bar chart { type: 'bar', encode: { x: 'date', y: 'volume' }, yAxisIndex: 1, tooltip: { formatter: (param) => `Volume: ${param.value[5]}`, }, }, // SMA line { type: 'line', encode: { x: 'date', y: 'sma50' }, yAxisIndex: 0, tooltip: { formatter: (param) => `SMA50: ${param.value[6]}`, }, }, ], });
Animated line chart
One of the cool things about Echarts is that you’re not limited to creating static pictures. Charts are animated, which for example lets you create line races like this:
Source code
const makeOptionsWithRandomData = () => { // randomized dataset with 4 columns const dataset = [['x', 'y', 'y2', 'y3']]; for (let i = 1; i < 25; i++) { dataset.push([i, i * Math.random(), i * Math.random(), i * Math.random()]); } return { // this will make the animation last 10000ms animationDuration: 10000, dataset: { source: dataset }, xAxis: { type: 'category' }, yAxis: {}, series: [ { type: 'line' }, { type: 'line' }, { type: 'line' }, ], }; } const race = echarts.init(document.getElementById('race')); race.setOption(makeOptionsWithRandomData()); setInterval(() => { // reset the chart with new random data race.clear(); race.setOption(makeOptionsWithRandomData(), true); }, 10000);
Interactive pie chart
The charts can also be made interactive using Javascript event listeners. Click on the chart below to change it from a Pie to a Treemap.
Source code
// steam players by editor and games const data = [ { value: 1568930, name: 'Valve', path: 'Valve', children: [ { value: 954936, name: 'Counter-Strike 2', path: 'Valve/Counter-Strike 2' }, { value: 613994, name: 'Dota 2', path: 'Valve/Dota 2' }, ], }, { value: 434978, name: 'Pocketpair', path: 'Pocketpair', children: [ { value: 434978, name: 'Palworld', path: 'Pocketpair/Palworld' }, ], }, { value: 286851, name: 'KRAFTON, Inc.', path: 'KRAFTON, Inc.', children: [ { value: 286851, name: 'PUBG: BATTLEGROUNDS', path: 'KRAFTON, Inc./PUBG: BATTLEGROUNDS' }, ], }, { value: 147735, name: 'Electronic Arts', path: 'Electronic Arts', children: [ { value: 147735, name: 'Apex Legends™', path: 'Electronic Arts/Apex Legends™' }, ], } ]; const pieOptions = { tooltip: {}, series: [ { type: 'pie', universalTransition: true, // smooth transition between chart types data, // treelike data can't be passed to dataset.source }, ] }; const treemapOptions = { tooltip: {}, series: [ { type: 'treemap', universalTransition: true, data, }, ] }; let isPie = true; const map = echarts.init(document.getElementById('map')); map.setOption(pieOptions); map.on('click', () => { // switch the options map.setOption(isPie ? treemapOptions : pieOptions, true); isPie = !isPie; });
Try it yourself
If you want to try it yourself, I suggest heading to the official tutorial. There you will find instructions about how to set up and start using Echarts, as well as how to customize it to fit into your existing design systems.
As there are many features I didn’t showcase in this article (like 3D graphs), I also recommend taking a look at the official examples.
-
Posted on
Setting up Mikochi with Docker and Traefik
Last year, I spent a little bit of time re-learning full-stack development and built Mikochi. The project has since grown to version 1.3.1 and reached 100 stars on GitHub. This article aims to be a step-by-step guide on how to install it and configure it to use HTTPS with Docker and Traefik.
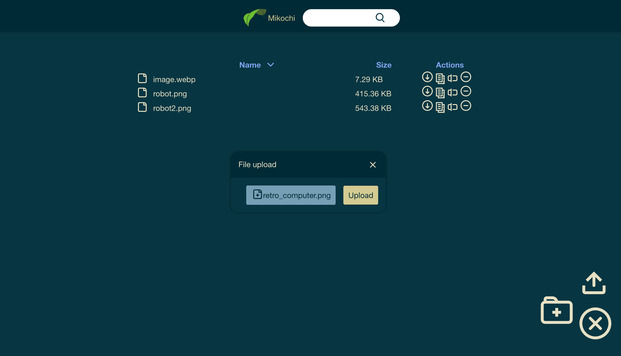
Preparation
First of all you, will need a Linux server. Mikochi was tested and works well on a 512MB RAM/1 vCPU virtual machine, so I recommend getting at least that. For this tutorial, I used Ubuntu 23.10, but it should also work on other distributions.
To install Docker, follow the instructions from the official docs. Or just run:
curl https://get.docker.com | shMikochi will need access to a folder on your hard drive to store and manage your files. I suggest just creating one in your home directory named
/data:mkdir dataLaunching Mikochi
The easiest way to launch Mikochi is to use docker-compose. Let’s create a
docker-compose.ymlfile with just enough to launch Mikochi:version: '3' services: mikochi: image: zer0tonin/mikochi:latest # for ARM (Raspberry Pi), use mikochi:latest-armv7 volumes: - ./data:/data ports: - 80:8080Running
docker compose up -dshould pull the latest Mikochi image, run it, mount thedatadirectory, and listen on port 80 (the default HTTP port). You should be able to access Mikochi by going to your server’s IP in your browser. You can log in using the default username and password combination: root/pass.To change this username and password, you can set environment variables on the mikochi container in your docker-compose.yml. For example:
environment: USERNAME: alice PASSWORD: correcthorsebatterystapleIf you want to access Mikochi using a domain name, you can also indicate it by setting up the
hostnamevalue in your service definition:hostname: your.host.nameSetting up Traefik
Traefik is a reverse proxy: it takes HTTP requests and forwards them to other applications. This can be very convenient if you have multiple services running over the same machine since the reverse proxy will take care of automatically routing each request to the right service.
For the most basic Traefik setup, we need to add a service to our docker-compose file to launch the Traefik container:
traefik: image: "traefik:v2.10" command: - "--providers.docker=true" - "--providers.docker.exposedbydefault=false" - "--entrypoints.web.address=:80" ports: - "80:80" volumes: - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro"Then we need to modify the
mikochiservice indocker-compose.ymlto remove the hostname and ports blocks, and replace them with labels used by Traefik:mikochi: image: zer0tonin/mikochi:latest environment: USERNAME: alice PASSWORD: correcthorsebatterystaple volumes: - ./data:/data labels: - "traefik.enable=true" - "traefik.http.routers.mikochi.rule=Host(`your.host.name`)" - "traefik.http.routers.mikochi.entrypoints=web"Running
docker compose up -d, should now launch both Traefik and Mikochi. Accessing your domain (or VM’s IP) with your browser should still show you the Mikochi file browser. But HTTPS is not there yet.
Hakumei & Mikochi is a great anime by the way HTTPS with Let’s Encrypt
The internet is a dangerous place, and transferring files over plain unsecured HTTP is not always a good idea. Switching to HTTPS used to be a hassle, but now you can obtain certificates for free from Let’s Encrypt, and to make things even better, we can just ask Traefik to do all the work for us.
Before going back to our docker-compose file, let’s create a
letsencryptfolder, that will be used to store certificates.mkdir letsencryptTo switch to HTTPS, first, you’ll need Traefik to listen on port 443 instead of 80. This is done by changing the flag
entrypoints.web.addressto 443 and making sure that docker-compose maps the 443 port correctly:ports: - "443:443"Next, we will need to tell Traefik to create a Certificate Resolver and call it
myresolver. This resolver will use a TLS challenge, which is in my opinion the simplest to use. Let’s Encrypt requires that give them a valid email for verification purposes. This is done by passing the following flags to traefik:- "--certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.tlschallenge=true" - "--certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.email=your@email.com" - "--certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.storage=/letsencrypt/acme.json"The certificate will be stored in
/letsencrypt/acme.json, so we need to mount the previously createdletsencryptdirectory:volumes: - "./letsencrypt:/letsencrypt" - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro"Lastly, we will need Mikochi to use
myresolver. This is done by thetraefik.http.routers.mikochi.tls.certresolverwith the valuemyresolver.Your final
docker-compose.ymlfile should look like this:version: '3' services: traefik: image: "traefik:v2.10" command: - "--providers.docker=true" - "--providers.docker.exposedbydefault=false" - "--entrypoints.web.address=:443" - "--certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.tlschallenge=true" - "--certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.email=your@email.com" - "--certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.storage=/letsencrypt/acme.json" ports: - "443:443" volumes: - "./letsencrypt:/letsencrypt" - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro" mikochi: image: zer0tonin/mikochi:latest environment: USERNAME: alice PASSWORD: correcthorsebatterystaple volumes: - ./data:/data labels: - "traefik.enable=true" - "traefik.http.routers.mikochi.rule=Host(`your.host.name`)" - "traefik.http.routers.mikochi.entrypoints=web" - "traefik.http.routers.mikochi.tls.certresolver=myresolver"Run
docker compose up -dto start both containers, wait a couple of minutes for the certificates to appear, and enjoy using Mikochi with HTTPS.
subscribe via RSS