Thoughts on releasing our first indie game
Two weeks ago we released Dice’n Goblins, our first game on Steam. This project allowed me to discover and learn a lot of new things about game development and the industry. I will use this blog post to write down what I consider to be the most important lessons from the months spent working on this.

The development started around 2 years ago when Daphnée started prototyping a dungeon crawler featuring a goblin protagonist. After a few iterations, the game combat started featuring dice, and then those dice could be used to make combos.
In May 2024, the game was baptized Dice’n Goblins, and a Steam page was created featuring some early gameplay screenshots and footage. I joined the project full-time around this period.
Almost one year later, after amassing more than 8000 wishlists, the game finally released on Steam on April 4th, 2025. It was received positively by the gaming press, with great reviews from PCGamer and LadiesGamers. It now sits at 92% positive reviews from players on Steam.
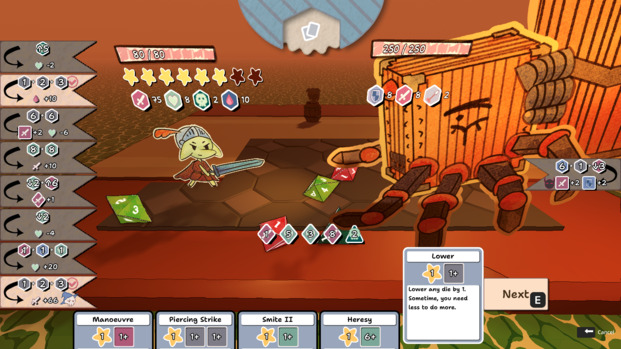
Building RPGs isn’t easy
As you can see from the above timeline, building this game took almost two years and two programmers. This is actually not that long if you consider that other indie RPGs have taken more than 6 years to come out.
The main issue with the genre is that you need to create a believable world. In practice, this requires programming many different systems that will interact together to give the impression of a cohesive universe. Every time you add a new system, you need to think about how it will fit all the existing game features.
For example, players typically expect an RPG to have a shop system. Of course, this means designing a shop non-player character (or building) and creating a UI that is displayed when you interact with it. But this also means thinking through a lot of other systems: combat needs to be changed to reward the player with gold, every item needs a price tag, chests should sometimes reward the player with gold, etc…
Adding too many systems can quickly get into scope creep territory, and make the development exponentially longer. But you can only get away with removing so much until your game stops being an RPG. Making a game without a shop might be acceptable, but the experience still needs to have more features than “walking around and fighting monsters” to feel complete.
RPGs are also, by definition, narrative experiences. While some games have managed to get away with procedurally generating 90% of the content, in general, you’ll need to get your hands dirty, write a story, and design a bunch of maps. Creating enough content for a game to fit 12h+ without having the player go through repetitive grind will by itself take a lot of time.
Having said all that, I definitely wouldn’t do any other kind of games than RPGs, because this is what I enjoy playing. I don’t think I would be able to nail what makes other genres fun if I don’t play them enough to understand what separates the good from the mediocre.

Marketing isn’t that complicated
Everyone in the game dev community knows that there are a lot of games releasing on Steam. To stand out amongst the 50+ games coming out every day, it’s important not only to have a finished product but also to plan a marketing campaign well in advance.
For most people coming from a software engineering background, like me, this can feel extremely daunting. Our education and jobs do not prepare us well for this kind of task.
In practice, it’s not that complicated. If your brain is able to provision a Kubernetes cluster, then you are most definitely capable of running a marketing campaign.
Like anything else, it’s a skill that you can learn over time by practicing it, and iteratively improving your methods. During the 8 months following the Steam page release, we tried basically everything you can think of as a way to promote the game. Every time something was having a positive impact, we would do it more, and we quickly stopped things with low impact.
The most important thing to keep in mind is your target audience. If you know who wants the game of games you’re making, it is very easy to find where they hang out and talk to them.
This is however not an easy question to answer for every game. For a long while, we were not sure who would like Dice’n Goblins. Is it people who like Etrian Odyssey? Fans of Dicey Dungeons? Nostalgic players of Paper Mario? For us, the answer was mostly #1, with a bit of #3.
Once we figured out what was our target audience, how to communicate with them, and most importantly, had a game that was visually appealing enough, marketing became very straightforward. This is why we really struggled to get our first 1000 wishlists, but getting the last 5000 was actually not that complicated.

Publishers aren’t magic
At some point, balancing the workload of actually building the game and figuring out how to market it felt too much for a two-person team. We therefore did what many indie studios do, and decided to work with a publisher. We worked with Rogue Duck Interactive, who previously published Dice & Fold, a fairly successful dice roguelike.
Without getting too much into details, it didn’t work out as planned and we decided, by mutual agreement, to go back to self-publishing Dice’n Goblins. The issue simply came from the audience question mentioned earlier. Even though Dice & Fold and Dice’n Goblins share some similarities, they target a different audience, which requires a completely different approach to marketing.
The lesson learned is that when picking a publisher, the most important thing you can do is to check that their current game catalog really matches the idea you have of your own game. If you’re building a fast-paced FPS, a publisher that only has experience with cozy simulation games will not be able to help you efficiently. In our situation, a publisher with experience in roguelikes and casual strategy games wasn’t a good fit for an RPG.
In addition to that, I don’t think the idea of using a publisher to remove marketing toil and focus on making the game is that much of a good idea in the long term. While it definitely helps to remove the pressure from handling social media accounts and ad campaigns, new effort will be required in communicating and negotiating with the publishing team. In the end, the difference between the work saved and the work gained might not have been worth selling a chunk of your game.

Conclusion
After all this was said and done, one big question I haven’t answered is: would I do it again? The answer is definitely yes.
Not only building this game was an extremely satisfying endeavor, but so much has been learned and built while doing it, it would be a shame not to go ahead and do a second one.